7491. Integer
Создайте класс Integer согласно следующей
диаграмме классов:
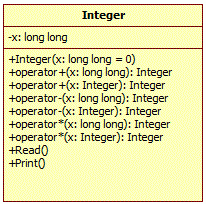
По заданным трем числам a, b, c вычислите значение выражения (a * 7 + b – 2) * (a – c + 5).
Вход. Одна строка содержит три числа a, b, c по модулю не больших чем 109.
Выход. Вывести значение
выражения.
|
Пример входа |
Пример выхода |
|
1 2 3 |
21 |
РЕШЕНИЕ
С++
классы
Анализ алгоритма
Для решения
задачи используем тип данных long long.
Реализация алгоритма
Читаем входные
данные. Вычисляем и выводим ответ.
scanf("%lld %lld %lld", &a, &b, &c);
res = (a * 7 + b - 2) * (a - c + 5);
printf("%lld\n", res);
Реализация алгоритма – класс Integer
#include <stdio.h>
class Integer
{
private:
long long x;
public:
Integer(long long x = 0) : x(x) {}
Integer operator+(long long x)
{
return Integer(this->x + x);
}
Integer operator+(Integer x)
{
return Integer(this->x + x.x);
}
Integer operator-(long long x)
{
return Integer(this->x - x);
}
Integer operator-(Integer x)
{
return Integer(this->x - x.x);
}
Integer operator*(long long x)
{
return Integer(this->x * x);
}
Integer operator*(Integer x)
{
return Integer(this->x * x.x);
}
void Read()
{
scanf("%lld", &x);
}
void Print()
{
printf("%lld\n", x);
}
};
int main(void)
{
Integer a, b, c, res;
a.Read(); b.Read();
c.Read();
res = (a * 7 + b - 2) * (a - c + 5);
res.Print();
return 0;
}
Реализация алгоритма – класс Integer
#include <stdio.h>
class Integer {
public:
Integer(long long x);
Integer operator+(long long x);
Integer operator+(Integer x);
Integer operator-(long long x);
Integer operator-(Integer x);
Integer operator*(long long x);
Integer operator*(Integer x);
void Read();
void Print();
private:
long long x;
};
Integer::Integer(long long x = 0) {
this->x = x;
}
Integer Integer::operator+(long long x) {
return Integer(this->x + x);
}
Integer Integer::operator+(Integer x) {
return Integer(this->x + x.x);
}
Integer Integer::operator-(long long x) {
return Integer(this->x - x);
}
Integer Integer::operator-(Integer x) {
return Integer(this->x - x.x);
}
Integer Integer::operator*(long long x) {
return Integer(this->x * x);
}
Integer Integer::operator*(Integer x) {
return Integer(this->x * x.x);
}
void Integer::Read() {
scanf("%lld", &x);
}
void Integer::Print() {
printf("%lld\n", x);
}
int main(void)
{
Integer a, b, c, res;
a.Read();
b.Read();
c.Read();
res = (a * 7 + b - 2) * (a - c + 5);
res.Print();
return 0;
}
Java реализация – classes, inheritance
import java.util.*;
class AddSub
{
public long add(long x, long y)
{
return x + y;
}
public long sub(long x, long y)
{
return x - y;
}
}
class Arithmetic extends AddSub
{
public long mult(long x, long y)
{
return x * y;
}
public long div(long x, long y)
{
return x / y;
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
Arithmetic ar = new Arithmetic();
long a = con.nextLong();
long b = con.nextLong();
long c = con.nextLong();
// res = (a *
7 + b - 2) * (a - c + 5)
long res = ar.mult(ar.add(ar.mult(a, 7), ar.sub(b, 2)), ar.add(ar.sub(a, c), 5));
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}